Explain B Cell Role With Antibody Mediated Immunity
Many pathogenic microorganisms and toxins can be rendered harmless by the simple attachment of antibodies. Luckily there are millions of them in our body so we can fight many different types of infection.
This B cell-mediated attenuation of exacerbated inflammatory response is associated with detectable levels of immunoglobulins in the recipient B cell-deficient mice but does not require the presence of B cell locally in the infected lungs suggesting a role for immunoglobulin-mediated endocrine immune regulation during M.
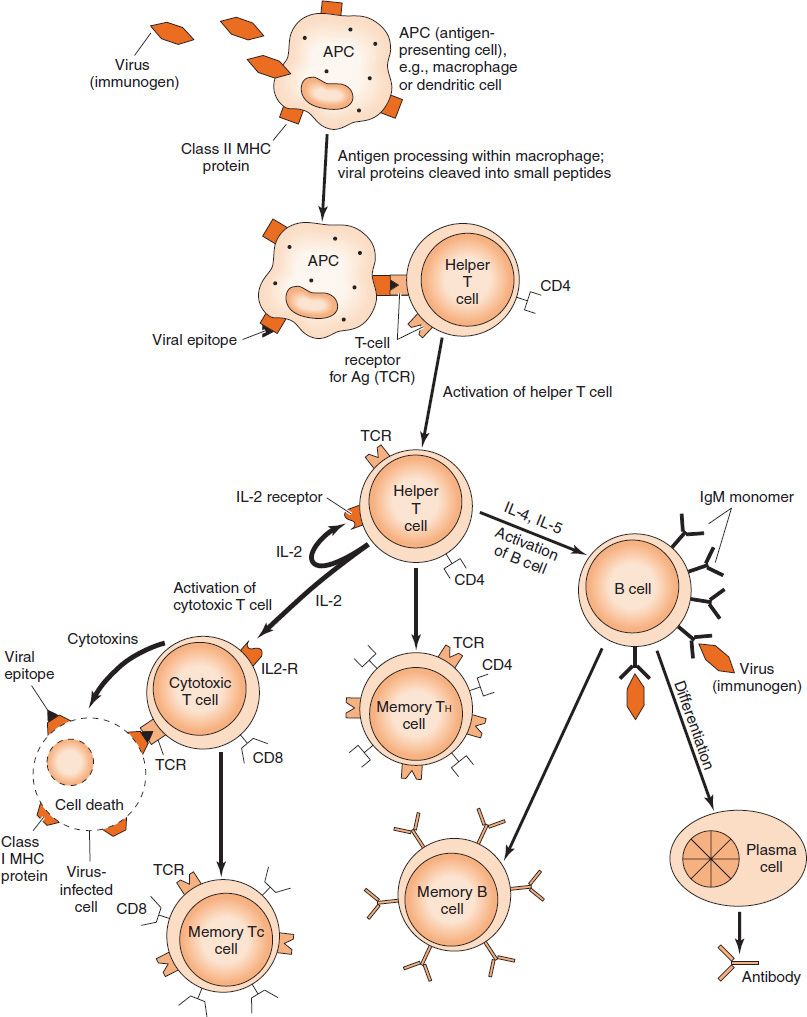
. Antibodies especially IgG that combine with such toxins neutralize them. They settle down mostly in the spleen and lymph nodes to pump out antibodies. The humoral response and the cell-mediated response.
This activates the B-cell. These plasma cells release antibodies in the bloodstream. Humoral immunity is immunity from serum antibodies produced by plasma cells.
In the presence of a foreign antigen specific B cells in lymph nodes spleen or mucosa-associated lymphatic tissue become activated. If the same antigen enters the body later the memory B cells divide to make more plasma cells and memory cells that can protect against future attacks by the same antigen. The B cell processed the cytokines and replicated them into more B cells the first differentiating into a memory B cell and the other into an antibody-producing plasma B cell.
Explain the role of B-cells B-lymphocyte within antibody-mediated immunity. Describe the mechanisms of T cell activation and differentiation. T H 2 cells initiate the humoral immune response by activating naive antigen-specific B cells to produce IgM antibodies.
Mature B cells have to modify their. The antigen is internalized by the B cell and presented on the helper T cell. Humoral immunity is the aspect of immunity that is mediated by macromolecules - including secreted antibodies complement proteins and certain antimicrobial peptides - located in extracellular fluidsHumoral immunity is named so because it involves substances found in the humors or body fluidsIt contrasts with cell-mediated immunityHumoral immunity is also.
Throughout the life of a B-cell it makes these antibodies. B cells differentiate into plasma cells which then produce antibodies. Explain B-cell B-lymphocyte role with antibody-mediated immunity.
Initially naïve B cells produce antibodies that remain bound to the cellular surface so that their exposed antigen-binding sites can detect potential pathogens toxins and foreign material. Explain B-cell B-lymphocyte role with antibody-mediated immunity. Each plasma B-cell makes antibodies to only one antigen.
Although the T-cell factor was nonantigen specific B-cell activation required the presence of both antigen and T-cell factor. 10 rows It shows a quick response against pathogens. B cells bone marrow-derived are responsible for antibody-mediated humoral immunity.
The B-cell co-receptor is composed of a subunit CD21 that binds complement fragments. Explain the role and importance of lymphocytes in the immune response. This surface-bound form of an antibody is known as an immunoglobulin.
T-helper and cytotoxic T-cells have a role in cell-mediated immunity. Click here for an animation on the immune response. The humoral response works via B cells that produce antibodies which bind to and effectively neutralize an invader so that it cant infect a cell.
Describe the role of lymph nodes and spleen in this process. They are very specific. Humoral immunity in particular secreted neutralizing antibodies is of central importance to protect the body against acutely cytopathic viruses whereas noncytopathic viruses have found ways of balanced coexistence with the immune system to avoid antibody-mediated elimination.
It is the major defence mechanism against extracellular. T-helper cells release cytokines that activate phagocytic cells which phagocytose and destroy infections. Describe the importance of the immunoglobulin receptors on the surface of B-cells.
Immunity refers to the ability of your immune system to defend against infection and disease. Also susceptible to simple antibody attachment are the many. Each B cell produces its own set of antibodies with unique antigen-specific binding sites.
When the T cells activate stimulate the B cells to divide into plasma cells this is called antibody-mediated immunity. The B-cell receptor and co-receptor cooperate in B cell activation -- explain. B-cells create antibodies that bind to antigens and neutralize bacteria.
Two arms of the adaptive immune system. They defend against antigens and pathogens in body fluids antibodies cant cross cell membranes. Antibodies and B cell memory in viral immunity.
The activated B cells grow and produce plasma cells. B cells in the lymph nodes spleen and other lymphatic tissue are responsible for antibody-mediated immunity b. Describe and distinguish between cell-mediated and antibody-mediated immunity and identify the cells responsible for each.
T H 1 cells activate the microbicidal properties of macrophages and induce B cells to make IgG antibodies that are very effective at opsonizing extracellular pathogens for uptake by phagocytic cells. B cells must continuously adapt A successful humoral immune response which is mediated by antibodies is dependent on several factors explains Di Virgilio. The memory B cells retain the information about the pathogen to prevent any disease caused by that pathogen in the near future.
There are two types of immunity that the adaptive immune system provides and they are dependent on the functions of B and T cells as described above. Click Antibody Mediated Immunity. The Immunity that is mediated by cells.
Similarities between Humoral Immunity and Cell-mediated Immunity. Thus it appears that although dependent upon T cells B lymphocytes may play an important role in amplification of cell-mediated immune responses. B Cell Activation Proliferation and Differentiation 2.
For example some harmful bacteria such as those that cause diphtheria and tetanus release toxins that poison essential body cells. Discuss the types of T cells and their roles in the immune response. B cells are involved in the humoral immune response which targets pathogens loose in blood and lymph and B cells carry out this response by secreting antibodiesT cells are involved in the cell-mediated immune response which targets infected cells in the body.
T cells include the Helper T cells and the Cytotoxic or Killer T cells. The adaptive immune system has two distinct approaches to destroying pathogens. One of the B cells allows the plasma B cell to spread the antibodies around the.
Given that the innate immune system deposits complement on pathogen this is recognized by the co-receptor -- bringing the cell into contact with the pathogen such that the BCR can bind to the epitope.

Humoral Immunity Is Antibody Mediated And Includes Antibodies That Tag A Pathogen For Destruction By Different Immunology Medical School Studying Nursing Study

Humoral Vs Cell Mediated Immunity Technology Networks
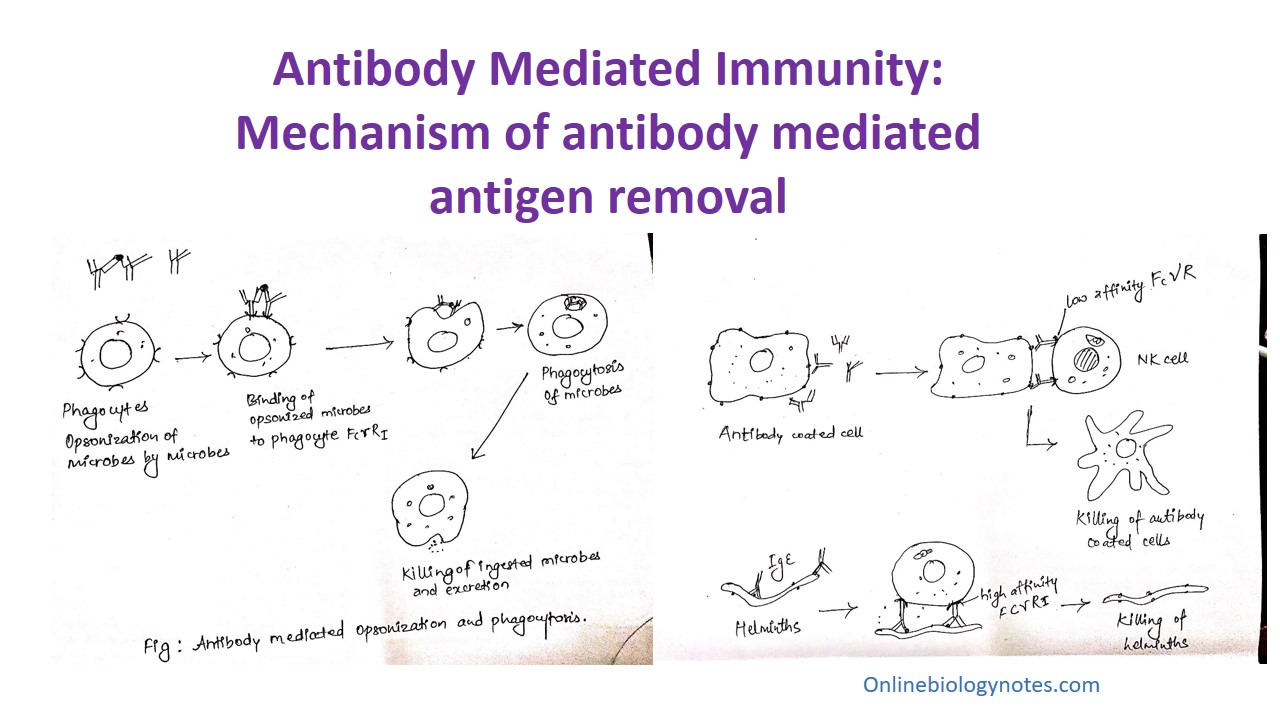
Antibody Mediated Immunity Ami Activation And Mechanism Of Antibody Mediated Antigen Removal Online Biology Notes

Humoral Response Read Biology Ck 12 Foundation

Humoral Vs Cell Mediated Immunity

Immune System Cell Diagram Mediated Immunity Humoral Immunity Cell Diagram Immune System Nursing Immunity Nursing

Antibody Mediated Immune Response Ami And Its Effector Mechanism Online Science Notes

Difference Between Cell Mediated And Antibody Mediated Immunity Compare The Difference Between Similar Terms

Humoral Mediated Immunity Immunology Medbullets Step 1

Steps In Humoral Immune Response Or Antibody Mediated Immune Response Immune Response Immune System Lesson Immunity

Clip Image002 Medical Laboratory Science Medical Laboratory Immune System

Antibody Mediated Immune Response Ami And Its Effector Mechanism Online Science Notes

Image Result For Compare And Contrast Innate And Adaptive Immunity Immune System Health Psychology Immunology

Antibody Mediated Immunity At Duckduckgo Immunity Mediation T Cell
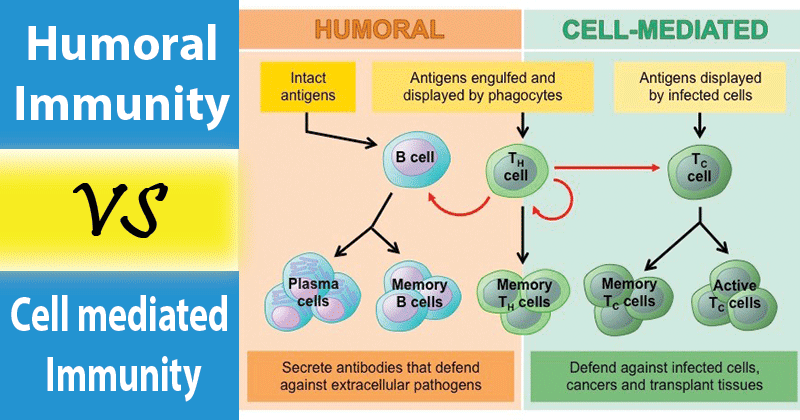
Humoral Vs Cell Mediated Immunity Definition 20 Differences

La Difesa Immunitaria Specifica Immune System Health Psychology Immunology


Comments
Post a Comment